Giacomo Lanzi
Giacomo Lanzi
Examples of phishing: the latest campaigns mentioned by the CSIRT
Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
Successful phishing attacks are increasing rapidly and so is the variety of forms they come in. Today I want to bring a couple of examples of phishing reported in the last period on the Italian territory by the CSIRT ( Computer Security Incident Response Team ).
Millions of users around the world are put at risk every day, statistically, one every 30 seconds. Cybercriminals are evolving and so are their techniques.
But it’s not just the traditional phishing scam that is catching on, but spear phishing and CEO fraud now also offer a much more damaging reach to the enterprise. For businesses, a successful attack could mean millions of dollars in damage.
Since it is known that users, even corporate users, tend to be lazy and do not manage their passwords effectively, even a phishing campaign aimed at individuals could provide useful credentials to later target corporate accounts. For this reason, one of the most effective defenses is the training of users, who, knowing the danger, can avoid it altogether.

Why does phishing work?
Before giving concrete examples of phishing that took place in Italy, it is interesting to understand why it is a technique that works so well. According to a white paper from Ostermann Research in 2017, phishing is the main concern of security teams.
There are 5 main reasons, identified by Ostermann Research, why phishing is still a real danger.
1. Lack of awareness
Undoubtedly, the predominant reason is the lack of “ security awareness “. More specifically, the lack of training on issues such as phishing and ransomware are the main reasons for the success of these attacks.
2. Need for more information
The use and notoriety of the Dark Web have lowered the commercial value of stolen data. The price of a credit card record dropped from $ 25 in 2011 to $ 6 in 2016 , which means that cybercriminals have had to adapt their attention to new ways to earn the amount of money they did in the past.
3. Lack of adequate protection
Companies are not doing enough to reduce the risks associated with phishing. There is a lack of proper backup processes, as well as an inability to identify weaker users who need further training.
In addition, there is a lack of strong control processes, such as double confirmation for every bank transfer request. Neglecting these protocols means putting yourself directly in the hands of some of the most common fraudulent techniques.
4. Ease of finding tools
The availability of phishing kits and the rise of ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) gave would-be hackers an easy opportunity to enter the market and compete with sophisticated criminal organizations.
The most troubling part of this growing trend is that even people with little or no computer experience are reaping the benefits of these easy-to-obtain tools.
5. Attacks leverage people’s weak points
As we have seen with social engineering , leveraging some factors can lower people’s guards . Alternatively, you aim for a sense of urgency to ensure that the necessary checks are not carried out before taking action. At other times it is guilt or shame that are used as a weapon to request money directly, as in the case of ransomware .
Among the examples of phishing that we will see shortly, I believe that the main factors for which they succeed are ignorance of IT (security) and feelings of guilt or urgency transmitted in the messages used in attacks.
Examples of 2021 phishing on Italian territory
“Eni gas and electricity reimbursement”
This campaign, reported in March 2021 , uses as a pretext a fake reimbursement from ENI Gas e Luce in order to steal personal data and banking information from the victims. The promise of a refund and seemingly legitimate web pages are key elements of the attack.
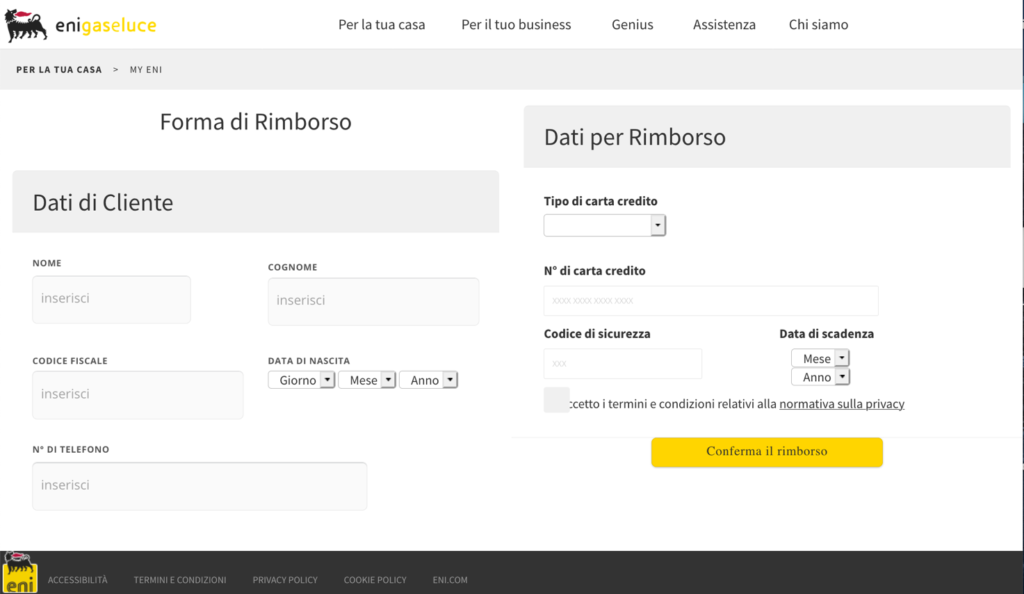
The following personal data are requested: name, surname, date of birth, social security number and telephone number. In addition, the following are also required: credit card type, number, expiration date and security code.
The victim reaches the phishing page by following a link to hxxps: //legendaryfirewitch.tumblr [.] com / eni , a page hosted on the Tumblr social platform. From here the user is redirected, using a Javascript script, to a page similar to the ENI website.
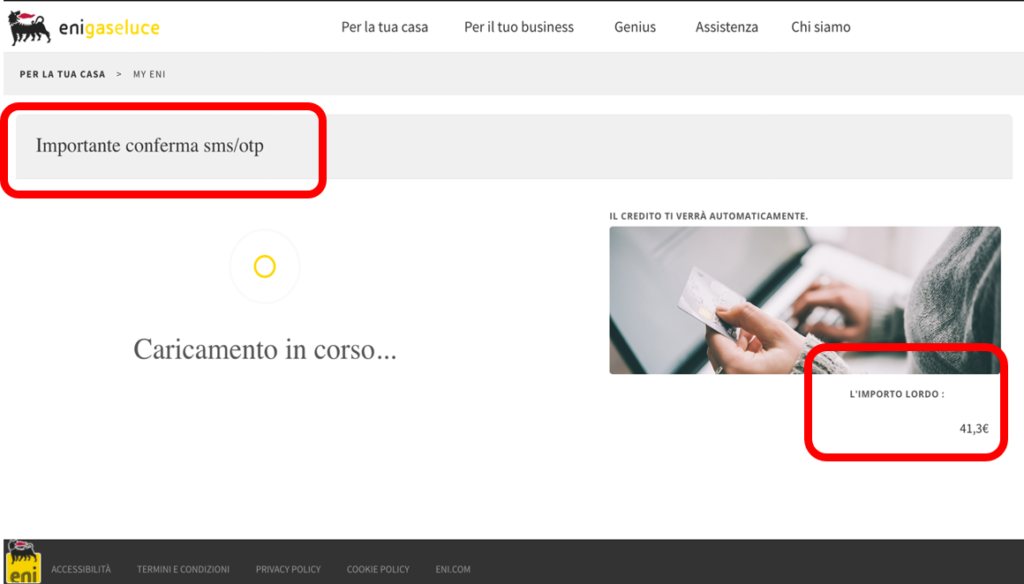
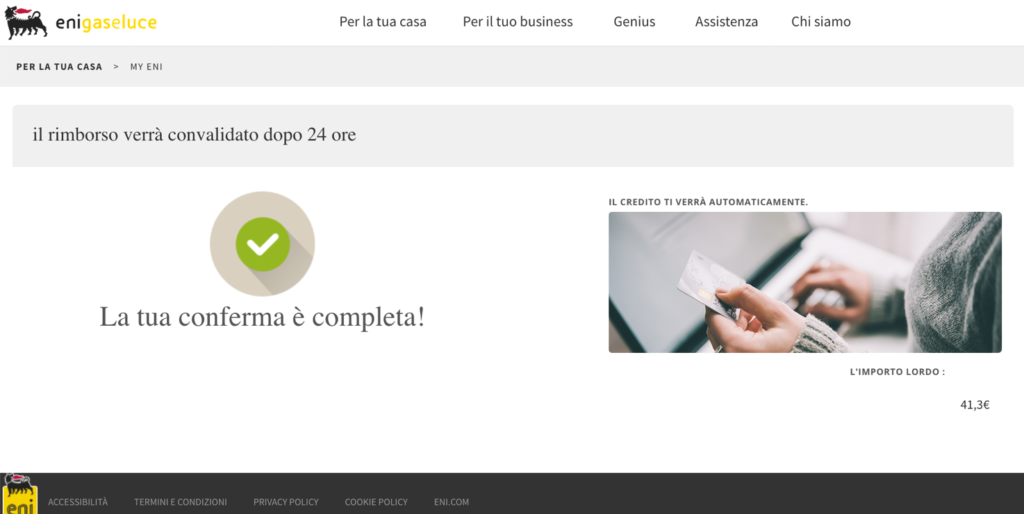
After entering the credentials in the form, two screens appear. A summary and a confirmation. Note that the SMS / OTP confirmation method is mentioned in the summary screen but is not required of the victim. Finally, you are directed to the real ENI website.
To defend yourself, always pay attention to the URLs of the pages you visit. These often contain elements of obvious wrongdoing. For example the ru extension of the pages.
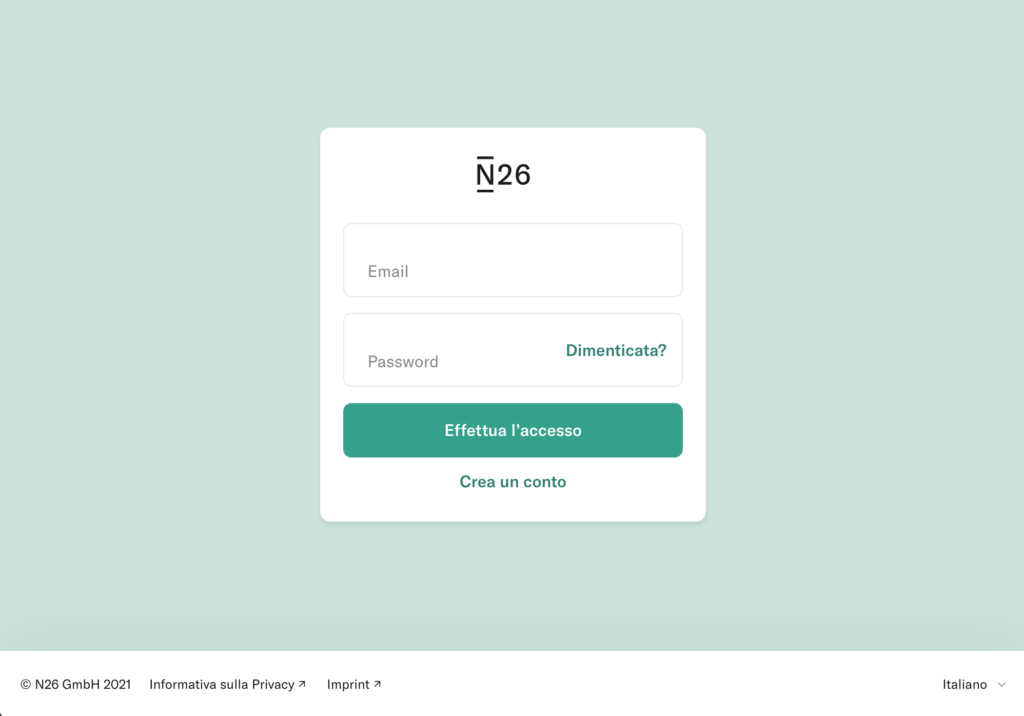
Bank Account Phishing Example (N26)
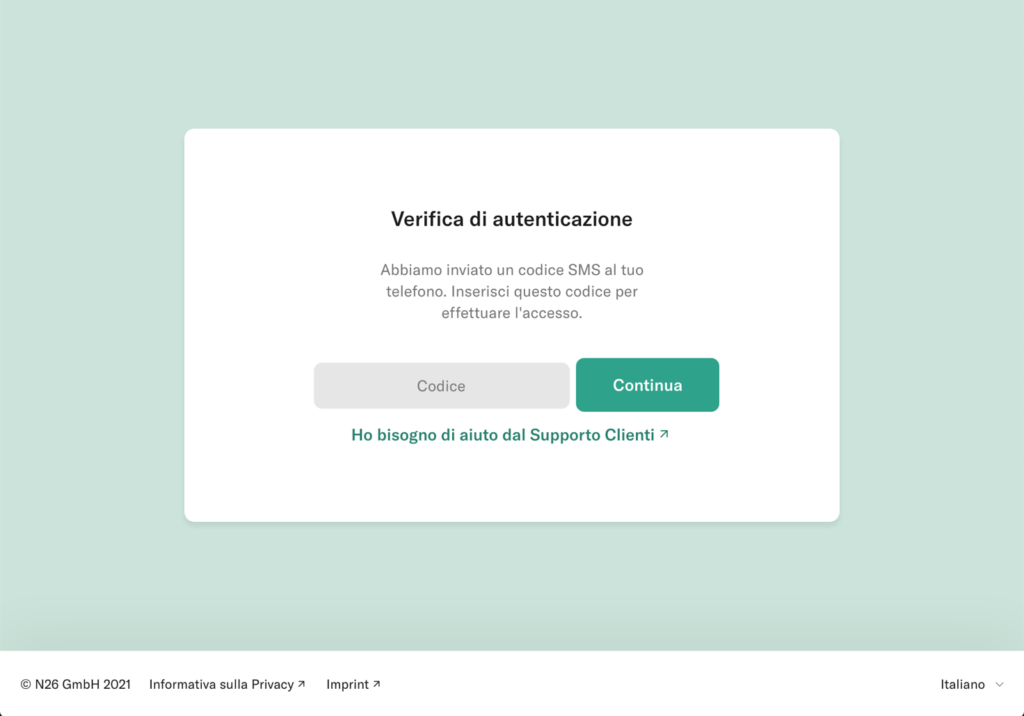
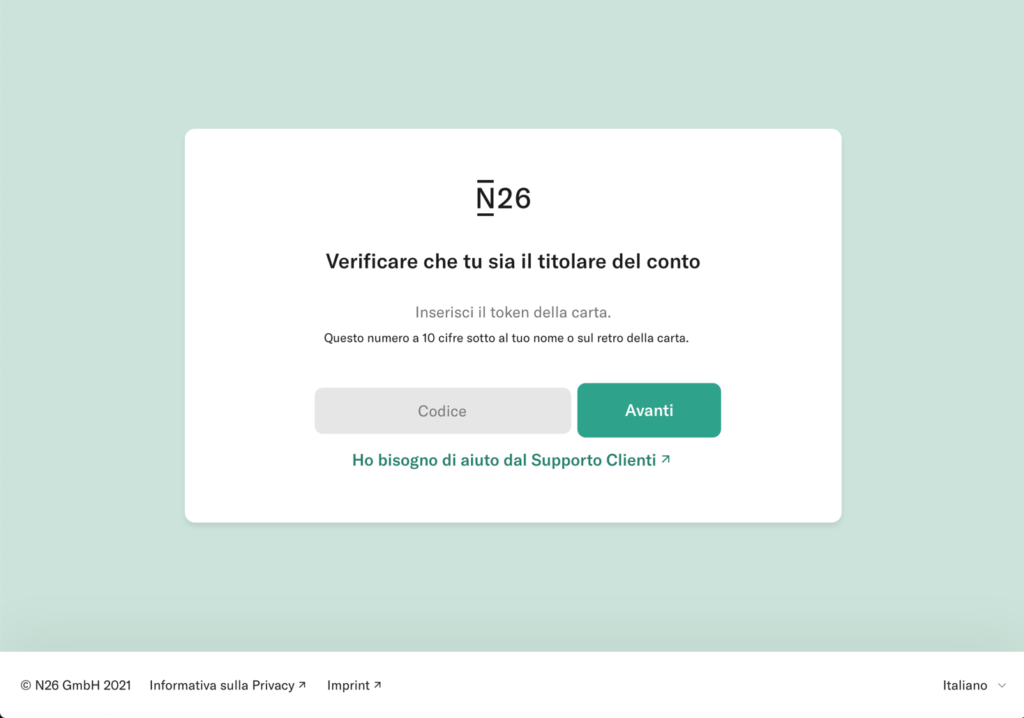
At the end of March 2021, a campaign affecting the customers of the N26 online bank was reported. Through SMS and email, users are asked for personal data, personal information (telephone number and social security number ) and the OTP code and the unique access token of the credit card.
Through a landing page very similar to that of N26, you are asked to log in to the service. The user enters the login credentials, the card code and then personal information is also requested. The excuse is to check the user’s data.
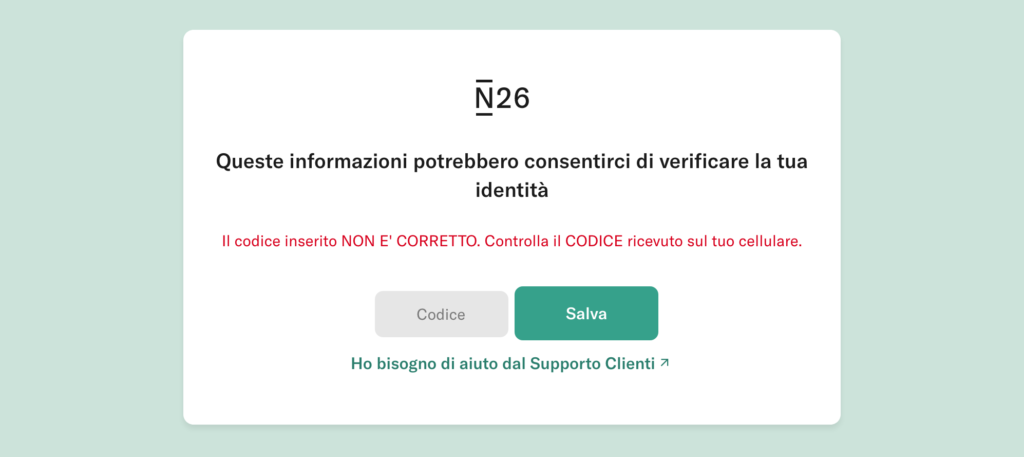
After entering the data, the victim is informed that the entered OTP code is incorrect and a new one is requested. This happens 3 times, until a server error page is shown.
The data has now been entered and sent to the attacker, who can access the victim’s account thanks to the information collected.
Conclusions
The phishing examples listed in this article are just two of all those regularly reported on the CSIRT site. Scams are often completely avoidable, if only you knew the basics of detecting a fraudulent web page.
Always valid advice: before following a link received, go to email, it is better to visit the site from your browser, without using the URLs provided in the message. Email communications are often notifications that must also be reflected on the account page on the site.
Those who fall victim to a phishing attack are likely not able to recognize threats in general. This can become a risk for the whole company.
The best defense is to invest in your employees. This can be done through ethical phishing campaigns followed by targeted training consolidate the problems found. At SOD, we can help your company recognize weaknesses and then provide employees with the information they need to raise the bar.
Contact us to find out how we can specifically help your company to raise the defenses against phishing and make the infrastructure more secure.
Useful links:
Useful links:
Customers
Twitter FEED
Recent activity
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes L'impatto crescente delle minacce informatiche, su sistemi operativi privati op… https://t.co/FimxTS4o9G
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes The growing impact of cyber threats, on private or corporate operating systems… https://t.co/y6G6RYA9n1
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Tempo di lettura stimato: 6 minuti Today we are talking about the CTI update of our services. Data security is… https://t.co/YAZkn7iFqa
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes Il tema della sicurezza delle informazioni è di grande attualità in questo peri… https://t.co/tfve5Kzr09
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes The issue of information security is very topical in this historical period ch… https://t.co/TP8gvdRcrF
Newsletter
{subscription_form_1}© 2024 Cyberfero s.r.l. All Rights Reserved. Sede Legale: via Statuto 3 - 42121 Reggio Emilia (RE) – PEC [email protected] Cod. fiscale e P.IVA 03058120357 – R.E.A. 356650 Informativa Privacy - Certificazioni ISO