 Giacomo Lanzi
Giacomo Lanzi
What is a Network Lateral Movement and how to defend yourself
During a cyber attack, hackers have only one goal in mind. This goal could be accessing a developer’s machine and stealing a project’s source code, analyzing emails from a particular executive, or extracting customer data from a server. All they have to do is log into the machine or system that contains the data they want, right? Not exactly. Actually, it’s a little more complicated than that. To achieve their goal, hackers are likely to break into a low-level web server, email account, or employee device, to name a few. From that node, they will move sideways (hence the name network lateral movement) to achieve their goal.
In fact, when attackers compromise a resource on a network, that device is almost never their final destination. In addition, the initial compromise rarely causes serious damage and may go unnoticed. Only if the security teams are able to detect a lateral movement before the attackers reach their intended goal, it is possible to prevent the data breach.
In this article, we will look at some of the more common types of network lateral movement and identify ways in which we can detect the attack and defend ourselves.
Understanding the network lateral movement
Lateral movement occurs when an attacker takes possession of a resource within a network and then extends its reach from that device to others within the same network. Let’s see it with an outline to help us understand better.
The perimeter of the infrastructure to be penetrated is represented with a horizontal line. The upper half represents what is outside the net, while what is below the line represents what is inside. In order for an attacker to enter the network, it must move vertically, ie from the outside to the inside (also called North-South traffic). But once a foothold has been established, it is possible to move sideways or horizontally, ie within the same network (called East-West traffic) to reach the final goal of the attack.
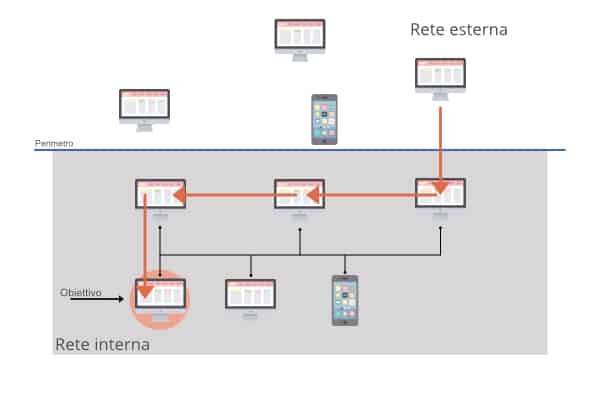
Possible path of a lateral movement. The arrow indicates the network nodes that are involved in the attack.
Approaches to the Lateral Movement
Overall, there are two common methods by which a hacker applies the lateral movement.
First approach: The attacker performs an internal scan to find out what other machines are on the network. In particular, it scans open ports that are listening and machines that suffer from vulnerabilities. At that point, the attacker can abuse these weaknesses to move sideways to another resource.
The second approach to the lateral movement exploits stolen credentials, and is the more common of the two. In this type of attack, the hacker could use an email phishing technique to infect a machine that interfaces with a particular server. Then he can use his login to recover passwords via a keylogger or other similar tools. At this point, he can use whatever credentials he was able to obtain to impersonate the user who was the victim of the phishing and log in to another machine. Once you have established access to that computer, you can repeat the tactic looking for additional credentials and / or privileges to exploit. In this way, the attacker can make their way and create remote connections to the target device.
In both cases it is difficult to identify the attack, because it does not occur through software or application malfunctions.
How to defend yourself
A lateral movement often manifests itself through anomalous network activity. For example, it is suspicious that a machine, which normally communicates with a few others, starts scanning the entire network. The same is true if that machine tries to connect to open ports, to interact with services and credentials with which it normally has no contact, or to use a username that has never been used before.
The list of alarm bells goes on and on. The key thing to understand is that a lateral movement involves machines doing something out of their routine, without proper authorization from IT.
This is what gives organizations the ability to detect this type of attack. Implementing log file monitoring is a first step in defense. Ideally, the data should be constantly analyzed for anomalies and possible breaches.
Defense issues
These defenses are not infallible. Security teams that simply rely on log files limit the scope of their defensive position, for example, due to log files collected only from particular applications. You might decide to monitor a certain service for credential theft, but attackers might not use that particular service to perform a lateral movement. This means that any malicious actions that do not use the monitored services will not be detected promptly.
In addition to this, hackers know the types of protocols that security personnel tend to monitor, making their task even more complex. Attackers can use this knowledge to model their attack campaigns in order to have a better chance of going unnoticed. It is one of the reasons why the MITER ATT & CK database was created to collect known techniques and raise the defenses.
The advantage of a SOCaaS
It is not enough for organizations to seek lateral movement using log files or an EDR tool. It is necessary to turn attention to the network as a whole. In this way it is possible to see all network traffic, establish a baseline of normal network activity for each user and device, and then monitor any unusual actions that could be indicative of attacks. It is known as anomaly detection, and is more comprehensive and often easier than examining each log file for out-of-the-ordinary events.
The problem with anomaly detection is that many of these irregularities are benign, and a lot of time is spent analyzing them. What is needed to separate harmful lateral movement from benign network anomalies is an understanding of the aspect of harmful behavior.
This is where a complete system that uses both behavioral analysis tools and professional security technicians comes into play.
The SOCaaS offered by SOD includes a Security Data Lake (SDL) for data collection and various tools for data analysis. One of these is the UEBA, particularly suitable for the detection of social threats, as it analyzes user behavior through AI using their actions as a source of data.
With these and other tools that make up the SOC, you can actively reduce the risk of attacks on your corporate data. If you are interested in learning more about SOD SOCaaS, I invite you to visit the dedicated page or contact us directly.
[btnsx id=”2931″]
Useful links:
Is SOCaaS useful for your business
Computer Network Security: PT vs. VA
Cyber Security: Pentest and verification of vulnerabilities
Customers
Twitter FEED
Recent activity
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes L'impatto crescente delle minacce informatiche, su sistemi operativi privati op… https://t.co/FimxTS4o9G
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes The growing impact of cyber threats, on private or corporate operating systems… https://t.co/y6G6RYA9n1
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Tempo di lettura stimato: 6 minuti Today we are talking about the CTI update of our services. Data security is… https://t.co/YAZkn7iFqa
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes Il tema della sicurezza delle informazioni è di grande attualità in questo peri… https://t.co/tfve5Kzr09
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes The issue of information security is very topical in this historical period ch… https://t.co/TP8gvdRcrF
Newsletter
{subscription_form_1}© 2024 Cyberfero s.r.l. All Rights Reserved. Sede Legale: via Statuto 3 - 42121 Reggio Emilia (RE) – PEC [email protected] Cod. fiscale e P.IVA 03058120357 – R.E.A. 356650 Informativa Privacy - Certificazioni ISO












